Overview¶
Replicator reads the binary log events, augments them with schema information and writes the augmented stream to the chosen output. The following replication targets are supported: STDOUT, Kafka and HBase.
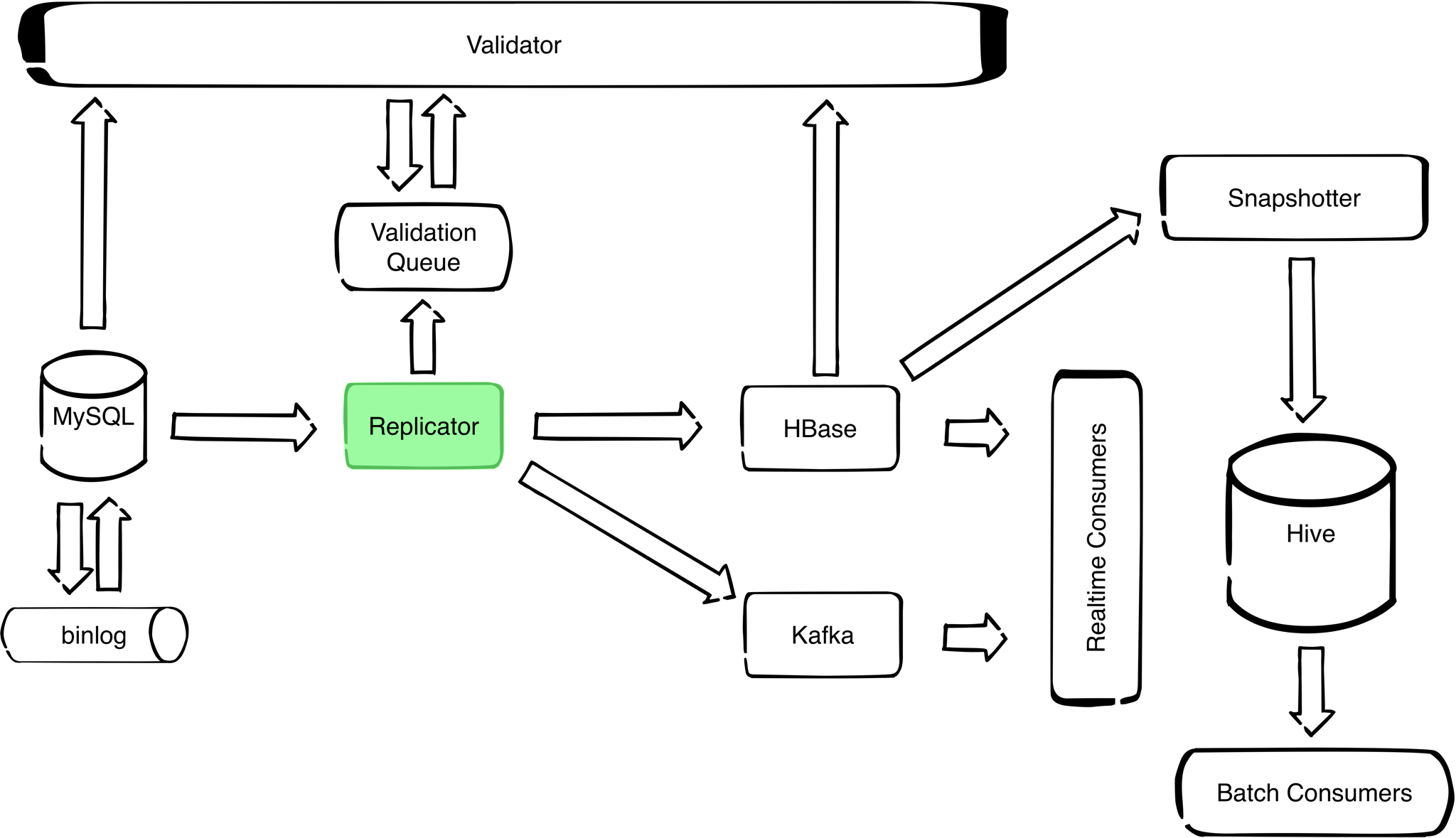
Before running the replicator, active schema needs to be initialized.
In addition, if you want to have the initial copy of the data (and not only the changes), you need to flush the contents of the database to the binlog.
Once that is done, you can proceed with configuring the replicator for the chosen replication target.
Stdout¶
This option is usefull for troubleshouting and debuging. In the command line parameters we specify applier as stdout, schema which needs to be replicated, starting binlog filename and path to th config file.
java -jar mysql-replicator.jar \
--applier STDOUT \
--schema $schema \
--binlog-filename $binlog-filename \
--config-path $config-path
Where the minimal configuration file is:
replication_schema:
name: 'testdb'
username: 'test_user'
password: 'test_pass'
host_pool: ['localhost']
metadata_store:
username: 'meta_user'
password: 'meta_pass'
host: 'localhost'
database: 'testdb_active_schema'
file:
path: '/path/on/disk'
metrics:
frequency: 10 seconds
reporters:
console:
timeZone: UTC
output: stdout
Where ‘testdb’ is a schema on local mysql instance that is going to be monitored for changes and ‘testdb_active_schema’ is a empty copy of ‘testdb’. By empty copy we mean a copy of the schema containing tables with no data. This copy can be created by mysqldump tool. An example is given in ‘Setup Active Schema’ section.
Example: assuming you have localhost database ‘testdb’ and have initialized active schema ‘testdb_active_schema’:
Create a test table:
CREATE TABLE `sometable` (
`pk_part_1` varchar(5) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`pk_part_2` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
`randomInt` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`randomVarchar` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`pk_part_1`,`pk_part_2`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Then run the replicator with:
java -jar mysql-replicator.jar \
--applier STDOUT \
--schema testdb \
--binlog-filename $starting-binlog-file-path \
--config-path $config-file-path
If you execute following sql in mysql shell:
insert into
sometable
(pk_part_1, pk_part_2, randomInt, randomVarchar)
values
('yOeTX','3371509','911440','jfOZXWuNyJVfOzpjbsoc')
You will see the following output (here it is given with jq pretty print, but in STDOUT it is compressed json) from the replicator:
{
"eventV4Header": {
"timestamp": 1494843484000008,
"eventType": 23,
"serverId": 1,
"eventLength": 65,
"nextPosition": 510,
"flags": 0,
"timestampOfReceipt": 1494843484220
},
"binlogFileName": "mysql-bin.000001",
"rowBinlogEventOrdinal": 1,
"tableName": "sometable",
"primaryKeyColumns": [
"pk_part_1",
"pk_part_2"
],
"rowUUID": "d36af99b-52be-4700-86d0-8c503b50658b",
"rowBinlogPositionID": "mysql-bin.000001:00000000000000000445:00000000000000000001",
"eventColumns": {
"pk_part_1": {
"type": "varchar(5)",
"value": "yOeTX"
},
"randomInt": {
"type": "int(11)",
"value": "911440"
},
"pk_part_2": {
"type": "int(11)",
"value": "3371509"
},
"randomVarchar": {
"type": "varchar(32)",
"value": "jfOZXWuNyJVfOzpjbsoc"
}
},
"eventType": "INSERT"
}
Kafka¶
You need to have a kafka topic specified in the config file.
replication_schema:
name: 'replicated_schema_name'
username: 'user'
password: 'pass'
host_pool: ['host_1', ..., 'host_n']
metadata_store:
username: 'user'
password: 'pass'
host: 'active_schema_host'
database: 'active_schema_database'
# The following are options for storing replicator metadata,
# only one should be used (zookeeper or file)
file:
path: '/path/on/disk'
kafka:
broker: "kafka-broker-1:port,...,kafka-broken-N:port"
topic: topic_name
# tables to replicate to kafka, can be either a list of tables,
# or an exlcussion filter
tables: ["table_1", ..., "table_N"]
excludetables: ["exlude_pattern_1",..., "exclude_pattern_N"]
metrics:
frequency: 10 seconds
reporters:
# The following are options for metrics reporters,
# only one should be used (graphite or console)
graphite:
namespace: 'graphite.namespace.prefix'
url: 'graphite_host[:<graphite_port (default is 3002)>]'
console:
timeZone: UTC
output: stdout
Then you start the replicator:
java -jar mysql-replicator.jar \
--applier kafka \
--schema $schema \
--binlog-filename $binlog-filename \
--config-path $config-path
HBase¶
First step is seting up the config file, which needs to conaint the HBase zookeeper quorum
replication_schema:
name: 'replicated_schema_name'
username: 'user'
password: 'pass'
host_pool: ['host_1', ..., 'host_n']
metadata_store:
username: 'user'
password: 'pass'
host: 'active_schema_host'
database: 'active_schema_database'
zookeeper:
quorum: ['zk-host1', 'zk-host2']
path: '/path/in/zookeeper'
hbase:
namespace: 'schema_namespace'
zookeeper_quorum: ['hbase-zk1-host', ..., 'hbase-zkN-host']
# hive-imports is optional
hive_imports:
tables: ['sometable']
metrics:
frequency: 10 seconds
reporters:
# The following are options for metrics reporters,
# only one should be used (graphite or console)
graphite:
namespace: 'graphite.namespace.prefix'
url: 'graphite_host[:<graphite_port (default is 3002)>]'
console:
timeZone: UTC
output: stdout
Then you can proceed with setting up the initial snapshot. By initial snapshot we mean the copy of the MySQL database that we make in HBase. The reason is that unlike Kafka which only track changes, in HBase we want to have the entire history of database incuding the initial values. Once the inital snapshot is done we can turn on the replication.
Initial snapshot:
Initial snapshot is the copy of mysql tables made before the replication to hbase is started. To make initial snapshot, two steps are performed.
Flush the database to the binlog (using the binlog flusher tool): binlog flusher. After the binlog-flusher finishes the flushing, by default mysql replication is stopped.
Then, the flushed data is replicated to HBase using the replicator with –initial-snapshot option:
java -jar mysql-replicator.jar \
--hbase-namespace $hbase-namespace \
--applier hbase --schema $schema \
--binlog-filename $first-binlog-filename \
--config-path $config-path \
--initial-snapshot
After the initial snapshot has been made start the mysql replication with:
start slave;
After this command mysql will start to write to binlogs again.
Then start the replicator:
java -jar mysql-replicator.jar \
--hbase-namespace $hbase-namespace \
--applier hbase \
--schema $schema \
--config-path $config-path